Fiber Cabling Guide
Copper Cabling has been one of the most popular source of data transfer. Over the years, copper cable has evolved for faster and efficient data transfer long distances earlier. In the age of 5G, Today, copper wires are increasingly being replaced by fiber optic cables.
The fiber optic cables transmit information using light pulses, in contrast to copper cables, which use electric pulses. When compared to copper cables, fiber optic cables require less maintenance and can transmit information over long distances without the need of being strengthened. The part the signals transmitted by fiber optic cables also have a higher speed and have large information-carrying capacity. All these advantages are the reason why the communication industry is actively switching from copper cables to fiber optic cables.
These fiber optic cables are divided into different types based on the material used, refractive index and mode. Based on the material used, Optical fibers are divided into glass optical fibers and plastic optical fibers.
Glass Fiber Type
The glass optical fibers are usually made of silica and can transfer data at the rate of 100 Mbps which is a substantial transmission speed. They are quite delicate in nature, but still, they can withstand extreme temperature conditions. Glass optical fibers are favored for long-distance communication, as they exhibit a lower loss in signal strength. These fibers, however, cannot be cut, repaired or spliced and need trained technicians for their installation.
Plastic Optical Fiber
When it comes to plastic optical fibers or POF; they use polymethyl methacrylate or PMMA (acrylic) as their core material. They transfer data at a rate of 2.5 Gb per second. POF is also known as consumer fibers since they are easy to install and are low cost. Due to the attenuation and distortion characteristics of PMMA fibers, they are commonly used for low-speed, short-distance (up to 100 meters) applications. In addition to this, they are highly sturdy when bent or stretched. The POF however, exhibits propagation loss, and so they are preferred only for short distances but they are highly cost effective.
Refractive Index
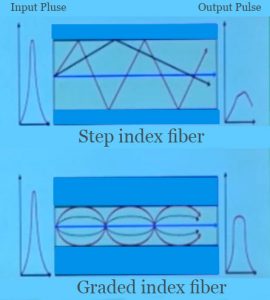
The final category for optical fibers is based on the mode. The mode determines the number of rays that can pass through the optical fiber at a given time. In this category fibers are divided into single mode and multimode fiber. In single mode fiber, only one ray of light travels at a given time. Single mode fibers are used for long distances, since they shown not disperse. Single mode fibers have small core diameters of about 10 mm and also are capable of carrying a higher bandwidth. In a multimode fiber. multiple rays of light traveled at a time, each having a different refraction angle. Multimode fibers are used for short distances sends the signals in them dispersed over long distances. The multimode fibers have a core diameter of about 50 micrometers, which allows multiple signals to propagate through the fiber. They carry a smaller bandwidth compared single mode fibers. For higher transmission rate and higher bandwidth transfer, one prefers single mode fibers. Depending upon the need for a long distance or short distance communication or whether multiple or single signals need to be transmitted, one can pick the desired optical fiber.
Singlemode and Multimode Fiber
The final category for optical fibers is based on the mode. The mode determines the number of rays that can pass through the optical fiber at a given time. In this category fibers are divided into single mode and multimode fiber. In single mode fiber, only one ray of light travels at a given time. Single mode fibers are used for long distances, since they shown not disperse. Single mode fibers have small core diameters of about 10 mm and also are capable of carrying a higher bandwidth. In a multimode fiber. multiple rays of light traveled at a time, each having a different refraction angle. Multimode fibers are used for short distances sends the signals in them dispersed over long distances. The multimode fibers have a core diameter of about 50 micrometers, which allows multiple signals to propagate through the fiber. They carry a smaller bandwidth compared single mode fibers. For higher transmission rate and higher bandwidth transfer, one prefers single mode fibers. Depending upon the need for a long distance or short distance communication or whether multiple or single signals need to be transmitted, one can pick the desired optical fiber.
If you planning a new network cable installation or considering upgrades to an existing network, you might want to consider using fiber Cabling Option as it offers Faster Speeds, can carry signals to longer distances, reliable and scalalble for future enhancements.





